 全球服务热线:400-086-8008
全球服务热线:400-086-8008- 日本语
 全球服务热线:400-086-8008
全球服务热线:400-086-8008

出国看病|美通过7T磁共振获得较详细人脑图像 呈现小于0.1毫米的脑组织
【本文为疾病百科知识,仅供阅读】 2019-07-17 作者:厚朴方舟
神外前沿讯,据美国《科学新闻》网站(sciencenews.org)7月8日报道,经过超过100小时的扫描,美国的研究人员,获得了迄今为止较为详细的整个人类大脑的三维图像。通过强大的7T磁共振(MRI),新图像的分辨率可以清晰呈现直径小于0.1毫米的物体。
扫描显示出杏仁体等大脑构造的生动细节,可以更深入地了解结构的细微变化与创伤后应激障碍等疾病之间的关系。
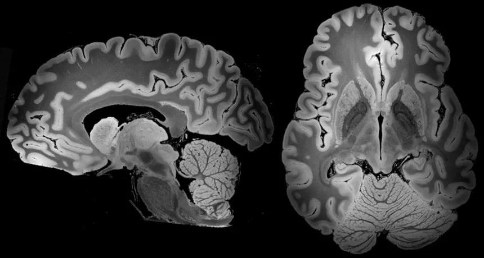
为了这项研究,波士顿麻省总医院和其他研究人员研究了一名死于病毒性肺炎的58岁女性的大脑。她捐赠的大脑,被认为是健康的,被保存和储存了将近三年。
7T功能强大、扫描时间长以及大脑处于高度静止状态,这些因素导致生成的图像分辨率极高。
研究人员试图找出与昏迷等病症和抑郁症等精神疾病有关的难以发现的大脑异常之处,而这些详细的大脑图像可为他们提供线索。这些图像“有可能增进对健康和患病人脑的结构的了解”。
Over 100 hours of scanning has yielded a 3-D picture of the whole human brain that’s more detailed than ever before. The new view, enabled by a powerful MRI, has the resolution potentially to spot objects that are smaller than 0.1 millimeters wide.
“We haven’t seen an entire brain like this,” says electrical engineer Priti Balchandani of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, who was not involved in the study. “It’s definitely unprecedented.”
The scan shows brain structures such as the amygdala in vivid detail, a picture that might lead to a deeper understanding of how subtle changes in anatomy could relate to disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder.
To get this new look, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston and elsewhere studied a brain from a 58-year-old woman who died of viral pneumonia. Her donated brain, presumed to be healthy, was preserved and stored for nearly three years.
Before the scan began, researchers built a custom spheroid case of urethane that held the brain still and allowed interfering air bubbles to escape. Sturdily encased, the brain then went into a powerful MRI machine called a 7 Tesla, or 7T, and stayed there for almost five days of scanning.
The strength of the 7T, the length of the scanning time and the fact that the brain was perfectly still led to the high-resolution images, which are described May 31 at bioRxiv.org. Associated videos of the brain, as well as the underlying dataset, are publicly available.
Researchers can’t get the same kind of resolution on brains of living people. For starters, people couldn’t tolerate a 100-hour scan. And even tiny movements, such as those that come from breathing and blood flow, would blur the images.
But pushing the technology further in postmortem samples “gives us an idea of what’s possible,” Balchandani says. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the first 7T scanner for clinical imaging in 2017, and large medical centers are increasingly using them to diagnose and study illnesses.
These detailed brain images could hold clues for researchers trying to pinpoint hard-to-see brain abnormalities involved in disorders such as comas and psychiatric conditions such as depression. The images “have the potential to advance understanding of human brain anatomy in health and disease,” the authors write.
厚朴方舟2012年进入海外医疗领域,总部位于北京,建立了由全球权威医学专家组成的美日名医集团,初个拥有日本政府官方颁发的海外医疗资格的企业。如果您有海外就医的需要,请拨打免费热线400-086-8008进行咨询!
本文由厚朴方舟编译,版权归厚朴方舟所有,转载或引用本网版权所有之内容须注明"转自厚朴方舟官网(www.hopenoah.com)"字样,对不遵守本声明或其他违法、恶意使用本网内容者,本网保留追究其法律责任的权利。
热门服务
推荐阅读
日本权威医学专家
日本医院排名
服务案例更多>
 全球咨询服务热线
全球咨询服务热线
400-086-8008

English | 微信端

互联网药品信息服务资格证书编号:(京)·非经营性·2015·0179
厚朴方舟健康管理(北京)有限公司 版权所有 www.hopenoah.com
京ICP备15061794号
京公网安备 11010502027115号